My car licence
International drivers
In Australia, motorists drive on the left-hand side of the road. For visitors that come from countries where motorists drive on the right-hand side of the road, this change in driving patterns can cause disorientation.
As a reminder, consider printing the DRIVE ON LEFT in Australia card (JPG, 59 KB) and putting it in your car where you can see it. You can also ask your hire car provider, tourism outlet or any Service SA customer service centre for a card and information about driving in South Australia. If you are a South Australian company providing services to visitors, you can order Drive on Left and road rule promotions.
Find South Australian road rules and safety tips in your country's language below.

Driving in South Australia
 | South Australian driver's licence lawsShort-term visitors with temporary visas can drive in South Australia. However, they must only drive the type of vehicle authorised by their licence. If you have a current driver's licence issued interstate or overseas, you must carry it at all times. If the licence is not in English, you must carry an International Driving Permit or an English translation. You must apply for a SA driver's licence if either:
|
| Keep leftIn Australia, you must drive on the left side of two-way roads. Ask passengers to remind you each time you set off and when you are turning at an intersection – it could save your life. When walking across the road, remember to look right, left and right again for traffic and cross only when safe to do so. |
 | Seatbelts and helmetsSeatbelts and child restraints must be worn where available in vehicles. Seatbelts reduce the risk of injury and death in a crash significantly. There are also heavy fines for not wearing a seatbelt or restraint. You must wear a crash helmet if you are riding on:
|

| SignsThis sign means you must stop and give way to all vehicles. Stop your vehicle just before the white stop line painted on the road. If there is no line, stop where you have a clear view of approaching traffic and give way to all vehicles approaching from your left and right. |
 | SpeedSpeed limits are strictly enforced in Australia. The speed limit is the maximum driving speed allowed. You must not drive above this limit. Some roads and streets don't have speed limit signs, but speed limits still apply. As a general rule, on roads where there are no signs but there are street lights or houses or other closely spaced buildings next to the road, the speed limit is 50 km/h. Where there are no signs or street lighting or houses or buildings next to the road, the speed limit is a maximum of 100 km/h in most states and territories. If the weather is poor (raining, fog) make sure you drive slower. All states and territories have mobile speed cameras, so slow down, drive safely and avoid heavy fines. |
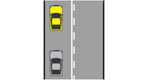 | Road markingsWhere the centre line marking on the road is one broken line, vehicles may cross the line to overtake when it is safe to do so. If the centre marking has two lines, you must not overtake if the line closest to your vehicle is unbroken. Where arrows are painted on the road, you must only drive in the direction they indicate. |
 | Alcohol and drugsDriving after you have consumed alcohol is dangerous. Australia has strict laws and penalties on drink-driving. Police actively enforce these laws and penalties through random breath testing programs. If you have a full driver's licence, you must not drive if your blood alcohol level is 0.05 per cent or higher. At 0.05 per cent blood alcohol concentration, your risk of being involved in a crash doubles. Driving after taking drugs that affect your ability to drive is illegal in all states and territories; penalties are severe. |
 | No mobile phonesYou are not permitted to use a handheld mobile phone when driving. This includes making or receiving calls, sending a text message, playing games and/or web browsing. |
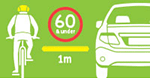 | CyclistsDrivers must give a minimum of 1 metre when passing a cyclist where the speed limit is 60 km/h or less, or 1.5 metres over 60 km/h. |
 | Driving tiredMany people die in crashes because the driver was tired. To avoid driving tired:
Rest areas are located every 80–120 kilometres on main roads for road users to pull over and rest when tired. Facilities may be limited but usually include seating, tables and shelter. If you are very tired, the only cure is sleep. |
 | Road conditionsRoad conditions can vary from a sealed surface to gravel and dirt. Use a four-wheel drive vehicle on unsealed roads in remote areas. Be careful of holes, soft road edges, narrow roads with unstable edges, narrow bridges, changing surfaces and dusty roads. The environment can change rapidly. Always check on local road conditions before leaving major roads. Turn your vehicle's headlights on low beam during the day, so vehicles can see you. Drive slowly on unsealed roads and take extra care – loose surfaces are unpredictable. If you drive off the side of the road, do not overcorrect, but slow down and return to the road when the vehicle is travelling at a safe speed. Obey road closure signs. Flooded roadsYou may come across water on the road. Roads may be covered in water which appears shallow but can have a current strong enough to sweep your vehicle away. Wait until the water level drops or use an alternative route. |
 | Driving in rural and remote AustraliaDriving in rural and remote areas requires special driving skills and awareness of different conditions. Make sure your vehicle is in good working order and has been serviced recently. Always carry a spare tyre, tools and water. If travelling to remote areas off major highways, take extra food, water, fuel and tyres. Our remote areas have few towns and facilities, often with large distances between them, so plan your trip. If travelling in remote areas or planning to leave major roads, tell local police of your intended route. AnimalsWatch out for animals on the road, such as kangaroos and emus. Livestock also graze on the side of unfenced roads. The most active time for many animals is sunrise and sunset. If an animal crosses in front of you, reduce speed safely and do not swerve violently. Otherwise, you may roll the vehicle. |
 | Road trainsHuge trucks, known as road trains, can be the length of 10 cars. It can take up to 2.5 kilometres to overtake a road train at 100km/h. Also allow plenty of room before you overtake as they may sway from side to side as you overtake. Be prepared for the 'windrush' when passing as it can pull you towards the road train. When being overtaken by a road train, maintain your speed and don't move off the road. Only slow once the road train moves out to pass. Make sure there is space for the road train between you and the vehicle in front of you. |
 | If your vehicle breaks downDo not leave your vehicle because it will provide you with shade and protection from the heat. Wait for help to come to you. Consider hiring appropriate emergency communication equipment. For example, a satellite phone and an Emergency Position Indicating Radio Beacon (EPIRB) device. |
 | Emergency assistance000 is the number for emergency services in Australia. They can connect you to Police, Ambulance or the Fire Brigade. You should only contact 000 in an emergency. |
More information
- Familiarise yourself with the Road Rules in South Australia in more detail.
- Contact the Royal Automobile Association (RAA) for advice about roadside assistance in South Australia.
- View Australian Explorer to find out about the distances between some of the major towns, cities and areas within and around South Australia. To find out about the distances between major interstate centres in Australia, use the Time and Distance Calculator.
- If heading towards the north of the state, check the temporary road closures, restrictions or warnings for outback roads.
- Visitors driving in South Australia are subject to the same penalties for road traffic offences as other drivers. More information on the penalties for road traffic offences.
- Check our safe driving tips.
- Travel safely in Australia